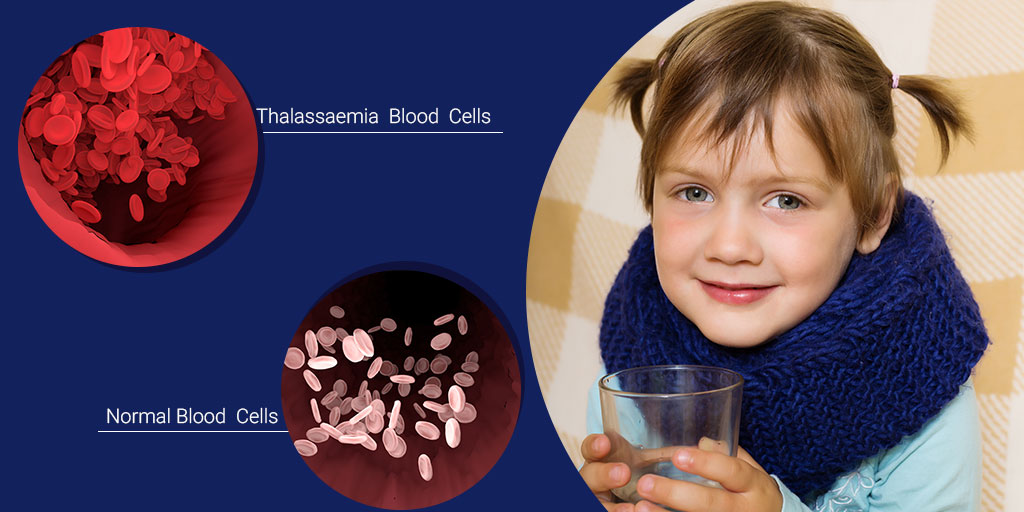
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder that emanates from the inability of the body to produce adequate amounts of hemoglobin, which often results in anemia and other complications. Presently thalassemia is a rather prevalent genetic disorder in India especially within specific regions hence, the need to seek effective treatment options available for patients. This article describes the best treatment options available for thalassemia in India. It emphasizes the necessity of early diagnosis and comprehensive care.
Understanding Thalassemia
Thalassemia primarily divides into alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia, with each type ranging from mild to severe. The most severe form of beta thalassemia is commonly known as thalassemia major. Symptoms include fatigue, lack of energy, weakness pale skin poor growth and in severe cases, organ damage.
Early Diagnosis
Diagnosis of thalassemia at an early stage plays an important role in the management of the disorder. It is possible to diagnose it through prenatal screening along with blood tests, which will also help in finding out the carriers. Newborn screening programs are also very important in covering all sections so that intervention could be provided at the right time. In India, too several hospitals and genetic counseling offer screening tests for the detection of thalassemia.
Treatment Options for Thalassemia
The line of treatment for thalassemia depends on the severity of the disease and, quite significantly the age of the patient. Here are some of the most common treatment options available in India:
1. Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusion is still the cornerstone of treatment in patients with severe thalassemia especially thalassemia major. This prevents anemia by maintaining adequate hemoglobin in the body improves quality of life and alleviates symptoms of severe anemia due to the disease. Most hospitals have associated blood banks that assure safe and timely transfusions.
Frequency of Transfusion: Transfusions are usually done every 2-4 weeks, according to the hemoglobin level and the needs of the individual patient. Monitoring which is essential to avoid complications such as iron overload might lead to irreparable organ damage with a cumulative effect.
2. Iron Chelation Therapy
One of the major complications with repeated transfusions is iron overload, wherein excess iron builds up within the tissues. This requires iron chelation therapy to prevent toxic effects. In India, many anemic agents are available that act effectively:
Deferasirox (Exjade): An effective oral chelator, which promotes the excretion of excess iron, used generally because it is easy to administer.
Deferoxamine (Desferal): Parenteral chelator; effective, but is requiring longer administration, often by infusion.
Chelation therapy is very important so that complications of iron overload, such as liver damage and heart disease, or diabetes can be avoided.
3. Folic Acid Supplementation
Folic acid plays a very important role in the synthesis of red blood cells. Most thalassemia patients are put on supplementary folic acid as part of their general management. In India this is usually added into the overall management of those patients who are on a transfusion program.
4. Bone Marrow/Stem Cell Transplantation
Currently, bone marrow or stem cell transplantation is the only possible cure for thalassemia and is entirely applicable to young patients and those with very severe forms of the disease. The surgical intervention replaces the diseased bone marrow with healthy functioning stem cells from a matching donor, preferably a sibling or occasionally some other compatible donor.
Eligibility: Not every patient can be a candidate for transplantation. The considerations involve age, the severity of the illness, and donor availability.
Success Rates: The success rates of stem cell transplantation have greatly improved and are particularly very promising when the transplant takes place at a young age.
A Number of hospitals in India, including those attached to some of the leading medical institutions, provide bone marrow transplant services. These are facilities that have the requisite expertise and technology in place for conducting such an ought-to-be-delicate procedure.
5. Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is an emerging treatment option for thalassemia. It aims to correct the genetic defect responsible for the disease by introducing a functional copy of the gene into the patient’s cells. While still in experimental stages, initial trials show promising results.
India is actively participating in research related to gene therapy, and some institutions are at the forefront of clinical trials. As advancements continue gene therapy may become a viable option for patients with thalassemia in the near future.
6. Supportive Care
Besides medical treatment, supportive care also plays an important role in the management of thalassemia. This includes the following:
Psychosocial Support: Through counseling and support groups, the patients and their family can manage emotional and psychosocial features of living with thalassemia.
Nutritional support can be enhanced by proper diet with proper balance of vitamins and minerals. Consultation from nutritionists will help provide the patients with proper dietary advice.
7. Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up
Thalassemia requires regular follow-ups for proper management. The patient should have routine checkups with respect to the level of hemoglobin and functioning of organs, which may need adjustments in each of the various treatments. The role of a healthcare professional is to inform the patients regarding self-care in terms of treatment schedules.
Conclusion
Thalassemia is a big health hazard in India, but by early diagnosis and timely management, patients can continue to lead healthy and productive lives. The treatment options available within the country include blood transfusion, iron chelation therapy, bone marrow transplantation and even gene therapy, which is an emerging option.
This is a condition that requires comprehensive care and frequent monitoring. However, since research is constantly being conducted and treatment options are expanding the outlook for thalassemia in India is now optimistic. There is a great need for awareness and education which will go a long way toward ensuring better outcomes. Hence, the call is for immediate involvement with healthcare providers for impacted families.