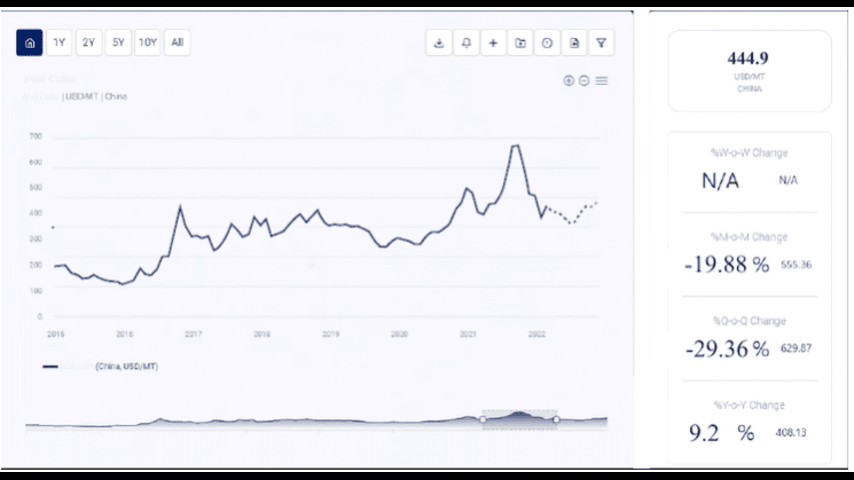
Threonine, an essential amino acid, is widely used in animal feed to optimize growth and improve protein metabolism, particularly in pigs and poultry. As a vital additive in animal nutrition, its demand is closely linked to the global feed industry. Additionally, threonine plays a role in various pharmaceutical and food industries, further driving its demand. The price of threonine, like many other commodities, is influenced by several factors including raw material availability, production costs, supply-demand dynamics, and macroeconomic trends.
In this article, we explore the threonine price trend, the factors influencing it, historical price movements, and future projections in the context of global markets.
Factors Influencing Threonine Prices
1. Raw Material Costs
Threonine is produced through fermentation processes, primarily utilizing raw materials such as glucose or starch. The cost of these raw materials significantly impacts the production cost of threonine, and any fluctuations in their prices can directly affect the final product’s price.
Glucose and Corn Prices
Glucose, derived from corn, is a major raw material for threonine production. Therefore, the price of corn heavily influences threonine costs. When corn prices rise, production costs for threonine increase, pushing up the price. Corn prices are volatile and can be affected by weather conditions, agricultural policies, and demand for biofuels, among other factors.
Impact of Weather and Crop Yields
Extreme weather events, such as droughts or floods, can lead to poor crop yields, reducing the availability of corn and other raw materials required for threonine production. This reduction in supply can drive up the prices of these raw materials, leading to higher threonine prices.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/threonine-price-trends/pricerequest
2. Supply Chain and Production Capacity
The supply chain for threonine is another critical factor influencing its price. Any disruptions in production capacity, transportation logistics, or global trade can cause fluctuations in supply, thereby affecting prices.
Production Facilities and Capacity Constraints
Threonine production is concentrated in a few countries, primarily China, which is the world’s leading producer and exporter of amino acids. Changes in production capacities, either due to technological upgrades or environmental regulations, can lead to shifts in supply. For example, if production plants undergo maintenance or face operational shutdowns due to environmental restrictions, the supply of threonine may decline, leading to price increases.
Transportation and Logistics
Threonine is traded globally, and transportation costs and logistics play a crucial role in determining its price. Rising fuel prices, port congestions, and logistical delays can increase the cost of shipping threonine, further affecting its market price. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has shown how vulnerable global supply chains can be to disruptions, causing fluctuations in the availability and price of many products, including threonine.
3. Global Demand for Animal Feed
Threonine’s primary application is in animal feed, particularly in livestock and poultry production. The demand for animal feed, therefore, directly affects threonine prices. Any changes in global meat production, livestock farming practices, or trends in animal nutrition can lead to shifts in the demand for threonine.
Expansion of the Livestock Industry
In recent years, the global livestock industry has seen steady growth, particularly in emerging markets like China, Brazil, and India. As the demand for meat products rises, so does the need for high-quality animal feed, driving up the demand for threonine and pushing prices higher.
Shift Toward Plant-Based Diets
While global meat consumption remains strong, there is a growing trend towards plant-based diets, particularly in developed markets. This shift could impact the demand for animal feed and subsequently lower threonine demand, which may lead to price stabilization or decreases in the future.
4. Technological Advancements
Advances in fermentation technology and amino acid production processes can influence threonine prices by lowering production costs and improving efficiency.
Improved Fermentation Processes
Recent innovations in microbial fermentation, genetic engineering, and process optimization have made it possible to produce threonine more efficiently. Companies that adopt these advanced production techniques can potentially reduce their production costs, resulting in lower market prices for threonine.
Automation in Production
The increasing use of automation in threonine production facilities can help reduce labor costs and improve consistency in production quality. As companies invest in automation, it could lead to a reduction in production costs over time, contributing to more stable or reduced prices for threonine in the long run.
5. Geopolitical and Trade Factors
Geopolitical events and international trade policies have a significant impact on threonine prices. Trade agreements, tariffs, and geopolitical tensions between major producing and consuming countries can cause price fluctuations in the global market.
Trade Tariffs and Restrictions
For example, trade tensions between the U.S. and China, two key players in the global agricultural and feed markets, have impacted the prices of various commodities, including threonine. Any imposition of tariffs or restrictions on imports and exports can disrupt the supply chain and lead to price fluctuations in importing countries.
Impact of Global Crises
The COVID-19 pandemic and the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict are examples of global crises that have caused significant disruptions in trade, production, and supply chains. Such events create uncertainty in the market, often leading to price hikes due to reduced supply or increased transportation costs.
Historical Price Trends of Threonine
1. Pre-2019 Period
Before 2019, threonine prices were relatively stable, with moderate fluctuations driven primarily by changes in raw material costs and demand from the animal feed industry. The global livestock sector was expanding steadily, and demand for amino acids, including threonine, remained strong.
2. 2019-2020 Period: Impact of African Swine Fever
In 2019, the outbreak of African Swine Fever (ASF) in China, the world’s largest producer and consumer of pork, had a significant impact on threonine prices. The disease led to a sharp reduction in the pig population in China, resulting in a decrease in demand for pig feed and, consequently, threonine. This led to a temporary decline in threonine prices during the first half of 2019.
However, as China started to rebuild its pig population in late 2019 and 2020, demand for threonine rebounded sharply, pushing prices upward. The recovery of the livestock sector, particularly in Asia, led to a surge in demand for amino acids, including threonine, driving price increases.
3. 2020-2021 Period: COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 caused widespread disruptions in global supply chains, affecting the production and distribution of many commodities, including threonine. Lockdowns, transportation restrictions, and labor shortages in key producing countries led to a reduction in threonine production, causing supply shortages and price increases.
By mid-2020, as the global economy began to recover and industries adapted to the new normal, threonine prices started to stabilize. However, continued logistical challenges, along with rising demand from the recovering livestock industry, kept prices elevated throughout 2020 and into 2021.
4. 2022-2023 Period: Market Recovery and Volatility
In 2022 and 2023, threonine prices remained volatile, primarily due to ongoing disruptions in the global supply chain, rising raw material costs, and geopolitical tensions. The Russia-Ukraine conflict exacerbated the already strained supply chain, particularly affecting the availability of raw materials like corn, which is crucial for threonine production.
At the same time, global demand for animal feed continued to rise, particularly in emerging markets, leading to sustained high prices for threonine. However, prices began to stabilize towards the end of 2023 as supply chain issues were gradually resolved, and production levels returned to normal.
Future Projections for Threonine Prices
1. Short-Term Outlook
In the short term, threonine prices are expected to remain relatively high due to ongoing geopolitical uncertainties, rising energy costs, and raw material price volatility. The Russia-Ukraine conflict, in particular, is likely to continue affecting the availability and price of corn, driving up the production cost of threonine.
However, as global supply chains recover and production capacity increases, the price of threonine may stabilize in the coming months. The recovery of the global livestock industry is expected to drive sustained demand for threonine, supporting relatively high prices in the near future.
2. Long-Term Outlook
In the long term, threonine prices are expected to stabilize as technological advancements in production processes help reduce costs and improve efficiency. The adoption of automation, improved fermentation techniques, and the development of alternative raw materials could lead to lower production costs, allowing for more stable threonine prices.
Additionally, the global shift toward sustainable and eco-friendly production practices may create new opportunities for threonine producers to optimize their production processes, further contributing to price stabilization. As demand for high-quality animal feed continues to rise, particularly in emerging markets, threonine prices are expected to remain strong over the next decade.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Number: USA & Canada — Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK — Phone no: +44 7537 132103 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) — Phone no: +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA