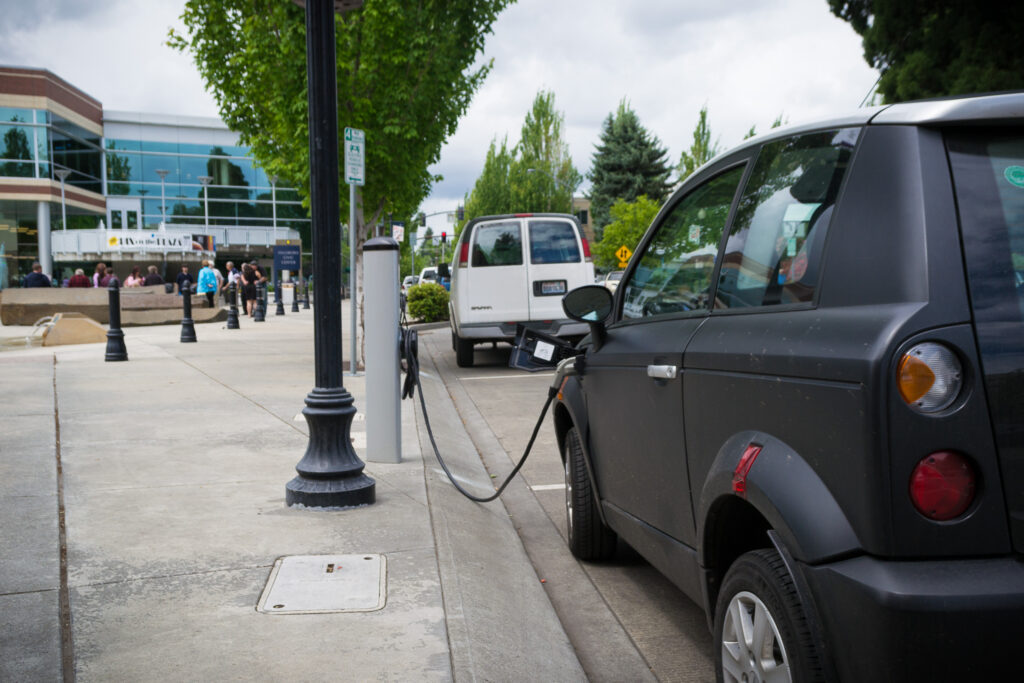As the world shifts towards a more sustainable future, cities are being required to adapt their infrastructure to accommodate electric vehicles (EVs). The rise of EVs is not just a trend but a significant change in how transportation operates. Governments and city planners are increasingly investing in infrastructure to support the growing number of electric vehicles on the road. This change is driven by the need to reduce carbon emissions, enhance air quality, and promote green energy. The adaptation to electric vehicle infrastructure is crucial for ensuring that urban areas can sustain this change while promoting environmental sustainability and economic growth.
The Growth of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles are becoming more common as consumers are drawn to their eco-friendly nature, lower operating costs, and advancements in technology. In recent years, the availability of different EV models has increased, offering consumers a variety of options to suit their needs. Governments worldwide are also incentivizing EV ownership by offering tax breaks, rebates, and grants, making electric cars a more affordable and attractive option for the public. This increase in demand has led to a pressing need for cities to adapt their infrastructure to support electric vehicles, as traditional fueling stations cannot meet the unique requirements of these cars.
Charging Stations: The Backbone of EV Infrastructure
One of the most critical elements of adapting cities to electric vehicles is the development of a robust network of charging stations. Without widespread access to charging points, electric vehicles cannot function efficiently, especially for long-distance travel. Cities are beginning to install charging stations in public areas, parking lots, and residential neighbourhoods to meet this demand. These charging stations vary in power, with some offering fast-charging capabilities that can significantly reduce the time it takes to recharge a vehicle. In some regions, governments are mandating that new buildings and parking structures include EV charging capabilities to future-proof urban infrastructure for the electric future.
The Role of Renewable Energy in Charging Infrastructure
As cities work to integrate electric vehicles, it is essential to consider the source of electricity used for charging stations. The environmental benefits of EVs can be diminished if the electricity used to power them is generated from non-renewable sources such as coal or gas. To maximise the positive impact of electric vehicles, many cities are focusing on connecting charging stations to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power. By aligning EV infrastructure with clean energy, cities can ensure that the transition to electric vehicles significantly reduces carbon emissions, contributing to a greener urban landscape.
Adapting Junkyards for the Future of Electric Vehicle Disposal
As cities adapt to electric vehicle infrastructure, the cash for damaged cars Sydney and junkyard industry must evolve to meet new demands. With the rise of electric vehicles, traditional scrapyards are shifting their focus to handle the recycling of electric car components, including batteries and rare metals. This transition not only supports sustainability efforts but also offers a valuable service in the disposal and recycling of electric vehicles, ensuring that cities can manage the growing number of outdated and unusable cars efficiently.
Impact on the Electrical Grid
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles presents new challenges for electrical grids, which must handle the increased demand for electricity. As more EVs are plugged into charging stations, cities face the risk of overwhelming their power supply if they are not adequately prepared. City planners and utility companies are working together to upgrade grids and ensure they can handle the additional load. In many regions, smart grids and energy management systems are being introduced to optimise electricity distribution. By implementing these advanced systems, cities can avoid power outages and ensure a consistent, reliable source of energy for both residential and commercial use.
Parking and Urban Space Considerations
With the growing need for EV charging stations, urban spaces must be redesigned to accommodate them. Cities are repurposing existing parking spaces to include EV charging points, particularly in densely populated areas where land is scarce. Some cities are exploring solutions such as installing curbside charging stations or integrating charging infrastructure into public transit hubs. These adaptations not only serve the current population of electric vehicle owners but also prepare cities for a future where EVs could be the dominant form of transportation. In the long term, the redesign of urban spaces to include EV infrastructure will help reduce congestion and pollution in cities.
Also visit: https://cashforcarsnsw.com.au/cash-for-unwanted-vehicles/
Collaboration Between Public and Private Sectors
The successful adaptation of cities to electric vehicle infrastructure requires collaboration between both the public and private sectors. Governments are working with private companies, including car manufacturers, utility providers, and charging network operators, to develop efficient and widespread EV infrastructure. This collaboration ensures that cities can meet the needs of electric vehicle owners while also promoting innovation and technological advancements in charging solutions. Private companies are often responsible for installing and maintaining charging stations, while governments provide incentives and regulatory frameworks to encourage the development of EV infrastructure.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While many cities have made strides in adapting to electric vehicle infrastructure, there are still significant challenges that need to be addressed. In some regions, the installation of charging stations is slow due to regulatory hurdles or lack of funding. Additionally, some cities lack the electrical grid capacity to support large-scale EV adoption. As more vehicles transition to electric power, the demand for raw materials used in battery production, such as lithium, could also pose a challenge to sustainability efforts. However, with continued innovation and investment, cities will likely overcome these obstacles. The future of urban transportation is electric, and cities that are proactive in their infrastructure development will be better positioned to support this transformation.
Conclusion
The shift toward electric vehicles represents a significant opportunity for cities to become more sustainable and reduce their environmental impact. By investing in EV infrastructure such as charging stations, renewable energy sources, and smart grids, cities can accommodate the growing number of electric vehicles while promoting green energy solutions. Though there are challenges to overcome, the collaboration between public and private sectors and continued technological advancements will ensure that cities are prepared for the electric future. As cities adapt to electric vehicle infrastructure, they are not only addressing the current needs of their residents but also laying the foundation for a more sustainable, eco-friendly urban environment.
Delve deeper into related topics.